General pattern of autosomal recessive inheritance
In the diagrams, gametes carrying the normal (wild) allele are in blue, gametes carrying the abnormal allele are in red. Sick people are in red, people who are not sick but carry the gene are in purple, people who do not carry the gene are in blue.
Union of a holder and a non-holder
As this diagram shows, with each pregnancy, this couple has a risk:
- 1/2 to have a child carrying the abnormal allele, he is said to be heterozygous
- 1/2 of having a non-carrier child who is said to be homozygous for the wild allele (normal)
So the transmission of an autosomal recessive genetic disease can stop (it is enough that no carrier child is born to the union).
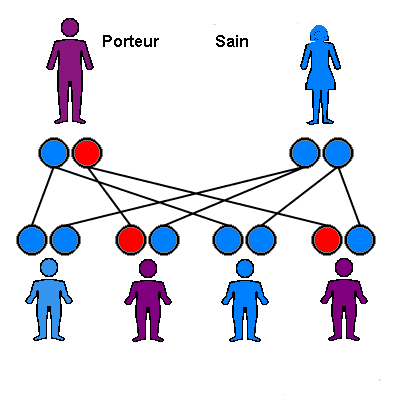
Union of two carriers
As the diagram below shows, with each pregnancy this couple has a risk:
- 1/4 to have a homozygous mutant child
- 1/2 of having a heterozygous child
- 1/4 of having a wild homozygous child
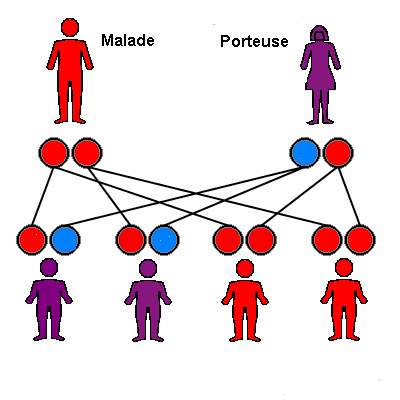
Union of a non-carrier and a patient
As the diagram below shows, all the children of this couple will carry the mutant allele

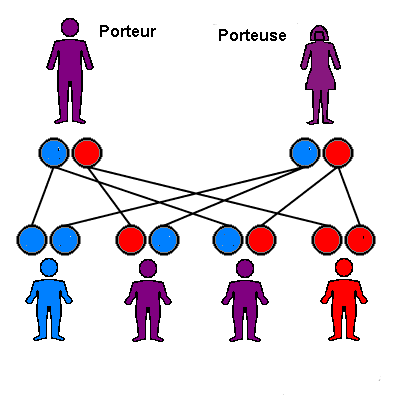
Union of a carrier and a patient
As the diagram below shows, with each pregnancy this couple has a risk:
- 1/2 of having a heterozygous child
- 1/2 to have a mutant homozygous child, therefore sick
Union of two patients
All the children are sick

